Version: CN
Have you heard of e-Invoices?
E-Invoices, short for electronic invoices, are replacing paper and electronic invoices.
It helps businesses work more efficiently and follow tax rules.
Recently, the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia has come up with the new guidelines for e-Invoice following the announcement of Budget 2024.
In this article, we’ll explore what e-Invoices are and everything you should know about them!
All you need to know about e-Invoice by LHDN
What is e-Invoice?
An e-Invoice is essentially an electronic version of a transaction record between a seller and a buyer.
It serves the same purpose as its paper or electronic predecessors, like invoices and credit or debit notes, but in a digital format.
Just like a traditional invoice, an e-Invoice includes critical details such as the names and contact information of the seller and buyer, a list of items or services provided, quantities, prices before tax, applicable taxes, and the total amount due.
This digital document is used to keep track of sales and purchases in everyday business activities.
Benefits of e-Invoice
Adopting e-Invoicing offers a smooth experience for taxpayers and enhances business operations while promoting adherence to tax regulations.

When will e-Invoices be implemented?
The introduction of e-Invoicing will occur in stages to ensure a smooth transition.
The implementation schedule has been strategically designed, considering various revenue thresholds, to give taxpayers ample time for preparation and adjustment.
Here’s the phased e-Invoicing implementation plan:
| Targeted Taxpayers | Implementation Date |
| Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM100 million | 1 August 2024 |
| Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM25 million and up to RM100 million | 1 January 2025 |
| All taxpayers | 1 July 2025 |
Scenarios and Types of e-Invoices
The e-Invoice setup is built to handle every aspect of billing and record-keeping digitally, dealing with a range of business situations and types of documents in a straightforward way.
Situations that require an e-Invoice
1. Proof of Income
Issued when a sale or transaction occurs to acknowledge the income of a taxpayer.
2. Proof of Expense
Pertains to the taxpayer’s purchases or expenditures, including returns and discounts. It’s also used for adjustments or deductions from recorded income.
Additionally, in certain cases, taxpayers must generate a self-issued e-Invoice to record expenses from international transactions.
The self-billed e-Invoice will be allowed for the following transactions:
- Payment to agents, dealers, distributors etc.
- Goods sold or services rendered by foreign suppliers
- Profit distribution (e.g. dividend distribution)
- e-Commerce transactions
- Payout to betting and gaming winners
- Acquisition of goods or services from individual taxpayers (who are not conducting a business)
For instance, if a taxpayer procures services from a foreign supplier who doesn’t utilize Malaysia’s MyInvois System, they must self-issue an e-Invoice to record the transaction.
Types of e-Invoices to be issued:
1. Invoice
A formal record detailing a transaction between a seller and a buyer, which may include self-issued e-Invoices for recording expenses like those from foreign suppliers.
2. Credit Note
Issued by sellers to rectify mistakes, grant discounts, or reconcile returns on a previously issued e-Invoice, aiming to decrease the value of the original e-Invoice without involving a cash refund to the buyer.
3. Debit Note
Created to reflect additional charges on an existing invoice.
4. Refund
An e-Invoice confirming the reimbursement of a payment to the buyer, applicable in instances where there is a monetary return to the purchaser.

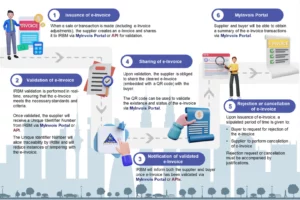
1. e-Invoice model via MyInvois Portal
MyInvois Portal contains all the functionalities required for taxpayers (supplier) to perform e-Invoice actions (i.e., generate, submit, view, cancel or reject invoice, etc.) and is specifically designed for the following purposes:
- Allows all taxpayers to view and search for their respective e-Invoices; and
- Provides MSMEs with the capability to issue e-Invoice and taxpayers who are not able to issue an e-Invoice on their own system.
Taxpayers are required to login to MyTax Portal to utilise MyInvois Portal to perform their e-Invoice obligations in accordance with the rules and requirements outlined by LHDN.
2. e-Invoice model via API
API allows taxpayers to submit e-Invoices directly to LHDN.
Taxpayers would need to configure the API integration by setting up call-backs (specific taxpayers system addresses) and log into the available LHDN APIs via the Digital Certificate issued by LHDN (authentication mechanisms).
The structure has been specifically designed to cater to B2B, B2G and B2C transactions to ease procedures for businesses and individual taxpayers.
There are 53 data fields that are required to issue an e-Invoice.
These fields are grouped into nine (9) categories:
- Address
- Business Details
- Contact Number
- Invoice Details
- Parties
- Party Details
- Payment Info
- Products / Services
- Unique ID Number
In addition, for specific circumstances, an annex will be required to be submitted as part of the e-Invoice to LHDN.
4. Does E-Invoice only apply to transactions within Malaysia?
No, it applies to transactions both within the country and across borders, including import and export activities.
5. Will every business need to use e-Invoice?
Yes, all businesses will need to use it, but the timeline for mandatory use depends on the business’s annual turnover or revenue threshold, following a phased implementation plan.
Find more frequently asked questions at the official LHDN website here.
Conclusion
Understanding different types of e-Invoices and the key information needed is important.
Embracing e-Invoicing means simplifying financial tasks and staying up-to-date in the digital world.
In IQI, we stay up to date with all the latest happenings and more. Join a company that encourages you to grow and learn as you go!
Continue reading:



