This article is contributed by Muhazrol Muhamad, GVP, Head of IQI IReality
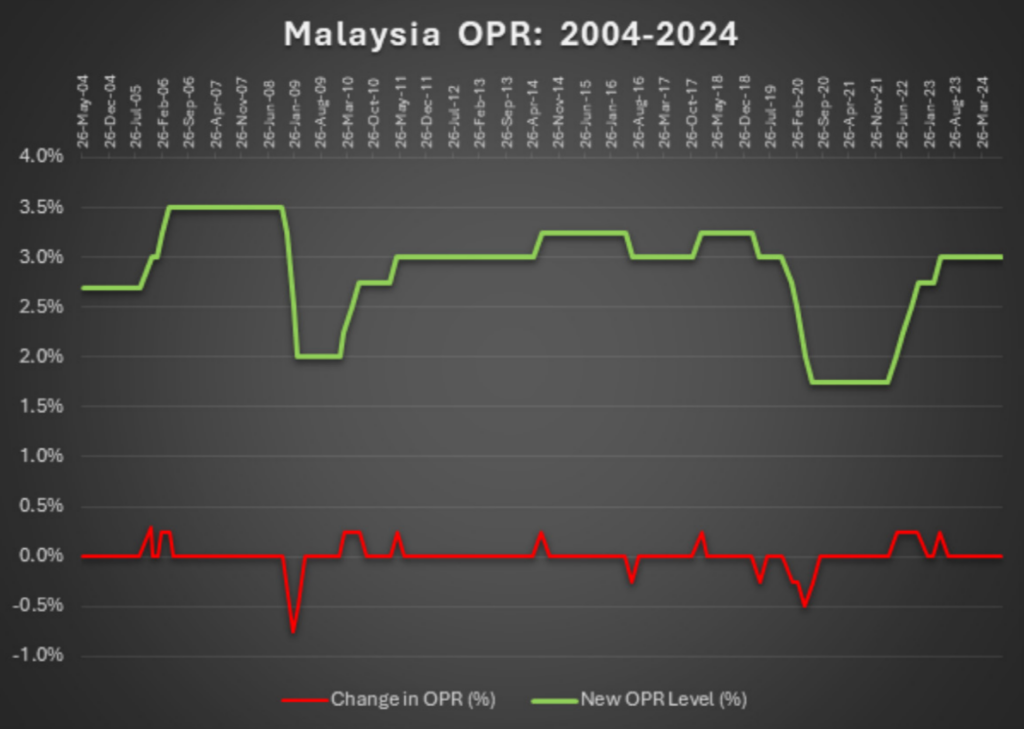
The Overnight Policy Rate (OPR), set by Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), plays a significant role in shaping economic activity in Malaysia, with its ripple effects profoundly impacting the real estate sector. Covering the period from 2004 through September 2024, the OPR’s trajectory offers insights into how monetary policy aligns with economic cycles and its direct implications for real estate, including housing affordability, investor sentiment, and market stability
The Current Economic Setting
As of the latest update in September 2024, the OPR remains stabilized at 3%, reflecting BNM’s strategy to maintain economic equilibrium amidst fluctuating global and domestic economic conditions. This approach demonstrates a nuanced understanding of the market’s needs, where excessively low rates might stoke inflation, and high rates could dampen
Sustainable Growth in the Property Market
This maintained rate, despite global economic recovery and localized market adjustments, suggests a commitment to fostering sustainable growth. For homebuyers, the stability in interest rates ensures predictable mortgage costs, making long-term financial planning more feasible. Similarly, for developers and investors, particularly in sectors like commercial real estate, such predictability supports more confident investment decisions, encouraging the progression of planned developments with reduced risk of abrupt financial shifts.
Adapting to Economic Predictability
The consistent OPR helps temper boom-and-bust cycles that can lead to real estate bubbles. With a steady rate, property prices tend to grow at a more sustainable pace, aligning more closely with actual demand and economic growth rather than speculative investment. This stability can help prevent the sharp corrections that have historically disrupted the real estate market and the broader economy.
Long-term Implications for Investors and Homebuyers
The period leading up to 2024 has shown that while the OPR is a powerful tool for economic management, its most effective application in the real estate sector is through moderation and foresight. By maintaining a stable OPR, BNM provides a foundation for both residential and commercial real estate markets to grow. For investors, particularly international ones, this signals a conducive environment for entering or expanding within the Malaysian market. For local homebuyers, it represents an opportunity to invest in property with confidence, knowing loan repayment conditions will remain stable and manageable over time.
Conclusion
The period from 2004 to 2024 has demonstrated the critical role of the OPR in shaping Malaysia’s economic and real estate landscapes. Looking forward, the lessons learned from past fluctuations provide valuable insights into the benefits of stability and measured adjustments. As Malaysia continues to navigate both domestic challenges and global economic trends, the OPR will undoubtedly remain a key focus of economic policy, playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of the nation’s real estate market.

